Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the foundation of modern electronics, and FR4 PCBs have become the industry standard for their manufacture. FR4 refers to a flame-retardant glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that is widely used in PCB manufacturing. Ucreate International’s technical department will guide you through FR4 PCBs, discussing the definition, importance and impact of FR4 materials on thermal performance and reliability.
What is FR4 PCB?
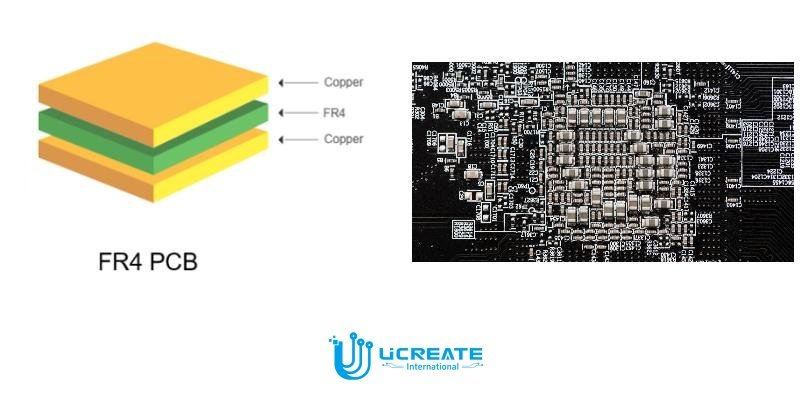
FR4 circuit board refers to a type of printed circuit board constructed using FR4 material as the base substrate. FR4 is a flame-retardant, glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that serves as the foundation for the PCB. The composition of FR4 PCBs typically consists of several layers of FR4 material with copper traces and components mounted on the surface.
The FR4 material itself is a combination of epoxy resin and woven glass fibre reinforcement. The epoxy resin provides electrical insulation, while the glass fibre reinforcement increases the mechanical strength and rigidity of the PCB. The layers of FR4 material are bonded together using heat and pressure to form a strong and durable substrate for the PCB.
Why is FR4 the most commonly used material for PCB manufacturing?

1. FR4 material performance and features
FR4 material has several properties and characteristics that make it highly suitable for the manufacture of printed circuit boards:
Electrical Insulation: FR4 has excellent electrical insulation properties, allowing it to prevent unwanted electrical leakage and short circuits between different PCB components and traces.
Mechanical strength: The glass fibre reinforcement in FR4 gives the PCB high mechanical strength and rigidity, making it resistant to bending, warping and mechanical stress during operation and handling.
Flame resistance: FR4 is inherently flame retardant, meaning it has the ability to resist the spread of flames and reduce the risk of fire hazards. This property ensures the safety and reliability of electronic equipment.
Dimensional stability: FR4 material has good dimensional stability, which means it retains its shape and size even when exposed to changes in temperature and humidity. This stability helps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of PCB assembly and component placement.
2. Advantages of FR4 PCBs
Availability: FR4 material is readily available from multiple suppliers, making it easily accessible to PCB manufacturers. Its popularity has led to a well-established supply chain, ensuring a reliable source of FR4 for high-volume production.
Cost Effectiveness: FR4 is a cost effective option compared to other high performance PCB materials. Its availability, ease of processing and compatibility with standard manufacturing processes contribute to its affordability, making it a preferred choice for a wide range of applications.
Process Compatibility: FR4 material is compatible with standard PCB manufacturing processes such as drilling, etching and soldering. It can be easily processed using conventional equipment and techniques, reducing manufacturing complexity and cost.
Versatility: FR4 PCBs can be used in a wide range of applications due to their electrical insulation, mechanical strength and flame-retardant properties. They are suitable for various industries including consumer electronics, telecommunications, automotive, industrial equipment and more.
3. How does FR4 material affect the thermal performance and reliability of PCB?
- Thermal Conductivity of FR4
The thermal conductivity of FR4 material is relatively low compared to specialised thermal management materials such as metal core PCBs or ceramics. This lower thermal conductivity affects the heat dissipation capabilities of FR4 PCBs. The FR4 substrate acts as an insulator, limiting the efficient transfer of heat away from heat-generating components on the PCB. As a result, FR4 PCBs can experience higher operating temperatures, leading to potential thermal stress on components and reduced overall thermal performance.
- Thermal Expansion and Stability
FR4 material has a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that can differ from that of certain electronic components, such as ceramic capacitors or surface-mounted devices (SMDs). This difference in CTE can lead to thermal mismatch stresses during temperature cycling, potentially causing solder joint failure, delamination or component damage. To mitigate these risks, proper design considerations, such as the use of thermal relief pads or controlled impedance structures, can help manage the effects of thermal expansion and ensure the reliability of FR4 PCBs.
- Heat Management Strategies
- Copper Plane and Thermal Vias: Increasing the copper plane area on FR4 boards improves heat dissipation. Thermal vias connected to copper planes facilitate heat transfer to internal layers or external heat sinks.
- Heat sinks and thermal pads: Attachments such as heat sinks or thermal pads can improve heat dissipation from high power components by providing a larger surface area for heat transfer.
- Thermal relief pads: These pads create a smaller copper area for soldering, reducing the heat sink effect during component assembly and improving solder joint reliability.
- Proper component placement: Careful consideration of component placement can minimise heat build-up by ensuring that heat-generating components are adequately spaced to reduce thermal interference.
While FR4 materials have limitations in terms of thermal conductivity, their impact on thermal performance and reliability can be managed through appropriate design considerations and thermal management strategies. Ucreate International’s design team can improve the thermal performance of FR4 PCBs by optimising component layout, heat dissipation and incorporating additional cooling techniques to ensure reliable operation and extended life in a variety of applications.

Conclusion
FR4 printed circuit boards based on FR4 materials play an important role in modern PCB manufacturing. The properties and characteristics of FR4, such as electrical insulation, mechanical strength and flame retardancy, make it the most widely used material in the industry. Despite its relatively low thermal conductivity, proper design considerations and thermal management strategies can optimise the thermal performance of FR4 PCBs.
Understanding the impact of FR4 on thermal performance and reliability is critical for PCB designers and manufacturers. While FR4 can limit heat dissipation compared to specialised thermal management materials, techniques such as increasing copper area, using thermal vias and employing heat sinks or thermal pads can improve heat dissipation. In addition, consideration of thermal expansion and stability during component placement and the use of thermal pads can reduce thermal stress and ensure reliability.
In particular, the mechanical strength and dimensional stability of FR4 contribute to the overall reliability of the PCB. However, specific application requirements and operating conditions should be carefully evaluated to determine if FR4 is suitable to achieve the required level of reliability.

 English
English
 中文
中文