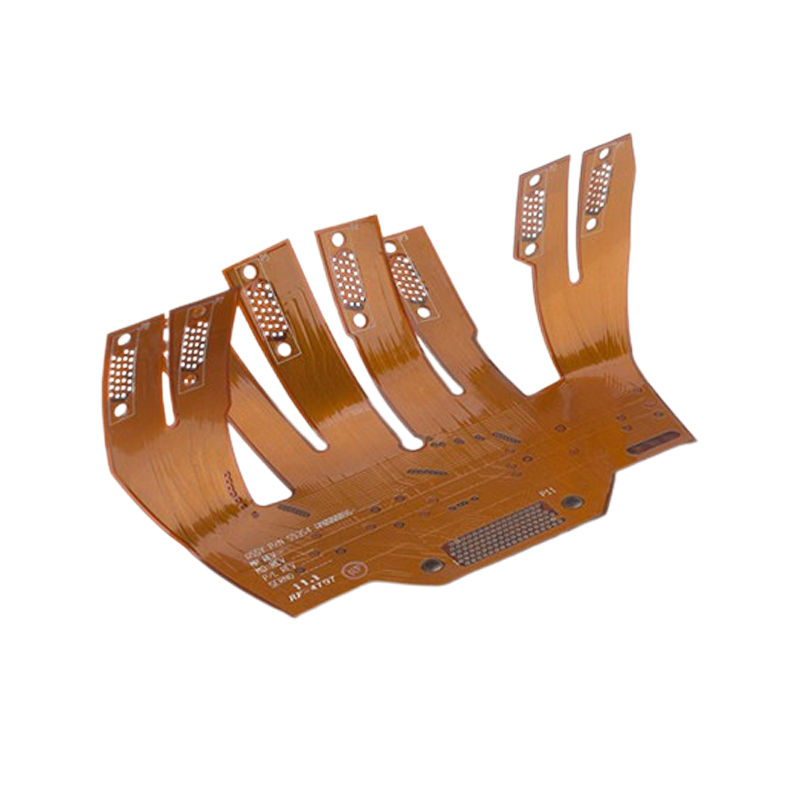
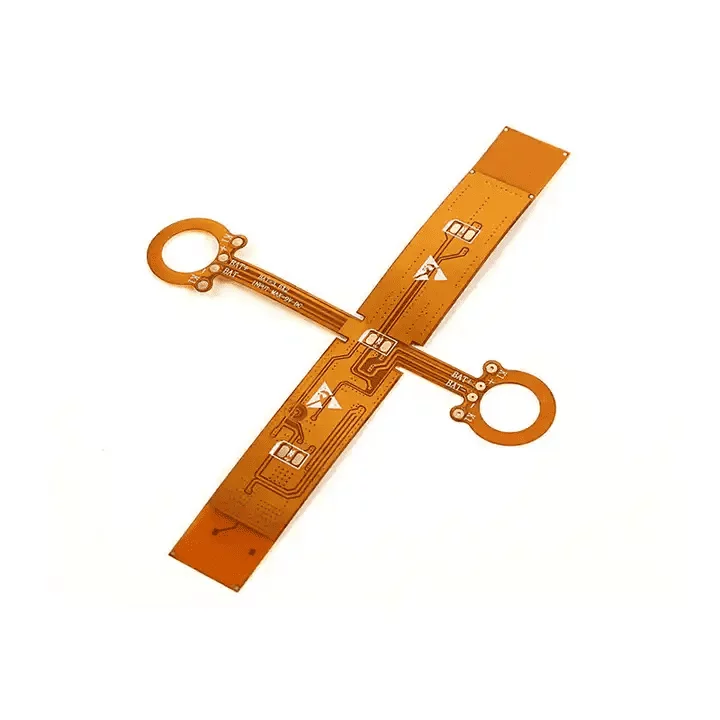
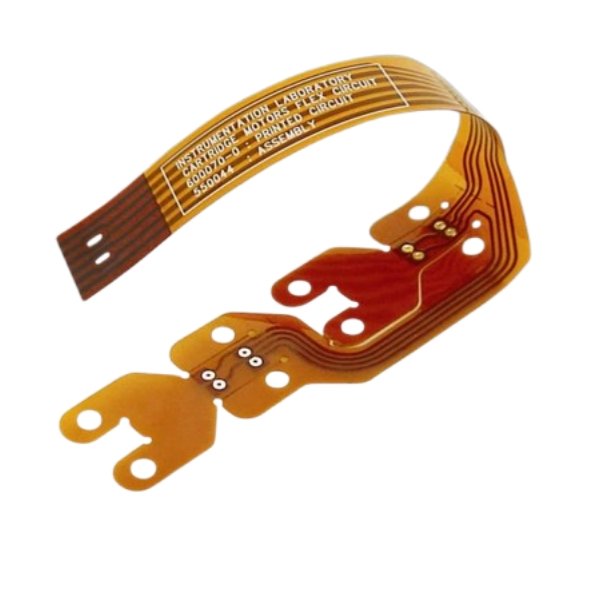
Flex PCB
| Item | Speci. |
|---|---|
| Layers | 1-4 layers |
| Board thickness | 0.07mm-4.0mm |
| Material | FR-4,CEM-1/CEM-3,PI,High Tg,Rogers |
| Max panel size | 220mm×500mm |
| Min hole size | 0.1mm |
| Min line width | 0.05 / 0.05mm |
| Surface finish | Plated Ni/Au, ENIG, Immersion Tin,Immersion Ag, OSP etc. |
| Copper thickness | 0.5-4oz |
| Soldermask | Green/Yellow/Black/White/Red/Blue |
| Silkscreen | White, Black, Blue, Green, Red etc. |
| Min PAD | 5mil(0.13mm) |
| Inter package | Vacuum |
| Outer package | Carton |
| Outline tolerance | ±0.1mm |
| Hole tolerance | PTH:±0.05 NPTH:±0.025 |
| Certificate | UL, IATF16949, ISO, RoHs&Reach |
| Special request | Blind hole+Gold finger + BGA |
| Material Suppilers | Shengyi, KB, Nanya, ITEQ,etc. |
If you have any requirements for PCB/ PCBA/Components, please contact us and we will reply to you as soon as possible!

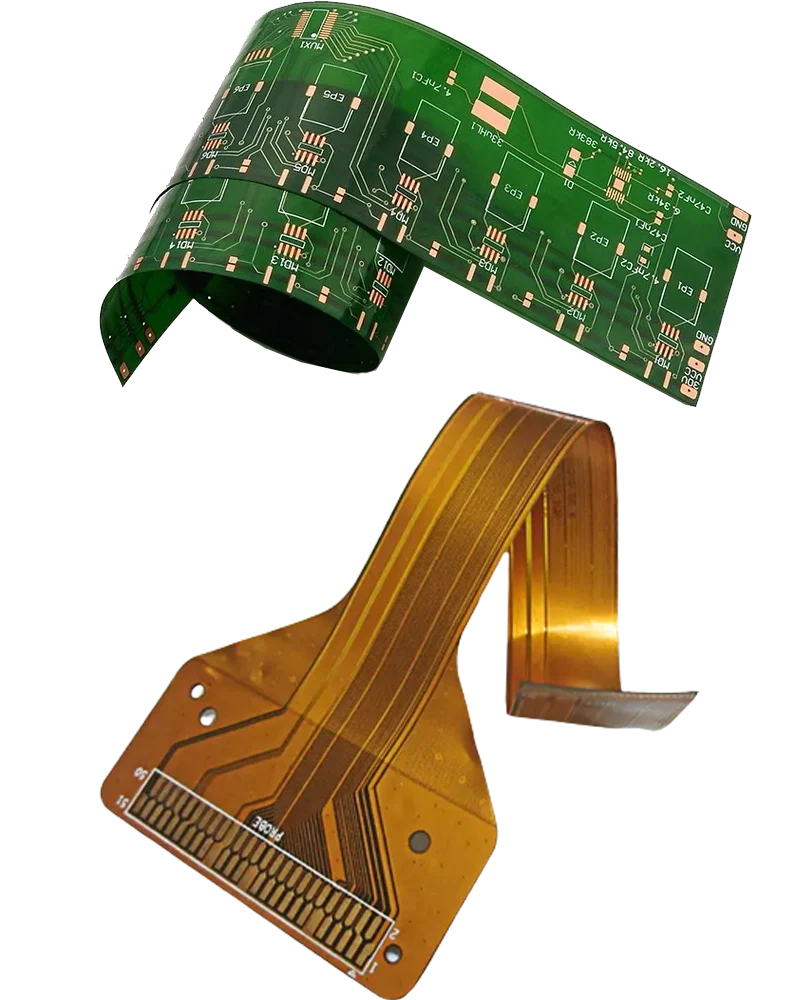
What Is Flexible PCB?
Flex PCB is defined as a patterned arrangement of PCB components utilizing a flexible base material and flexible sleeves (Flex PCB or FPC). Flexible Circuit Boards (also known as flexible circuit boards) derive their name from their ability to design a circuit to fit into any electronic device or product and incorporate it into a compliant circuit board. A flex circuit board is characterized by patterned arrangements of printed circuits that emphasize a malleable material base.
Flex electronics, also known as flex circuits, is a technology for mounting electronic circuits and electronic devices on flexible plastic substrates such as polyimide, peek, transparent conductive polyester and 1: 1 films. Flex circuits can be used in a variety of applications where flexibility and space-saving production constraints limit usability of rigid circuit boards as well as manual cabling and connectors. Flexible electronic assemblies can produce identical components with rigid circuit boards that fit into the desired shape when using the flexible circuit board.
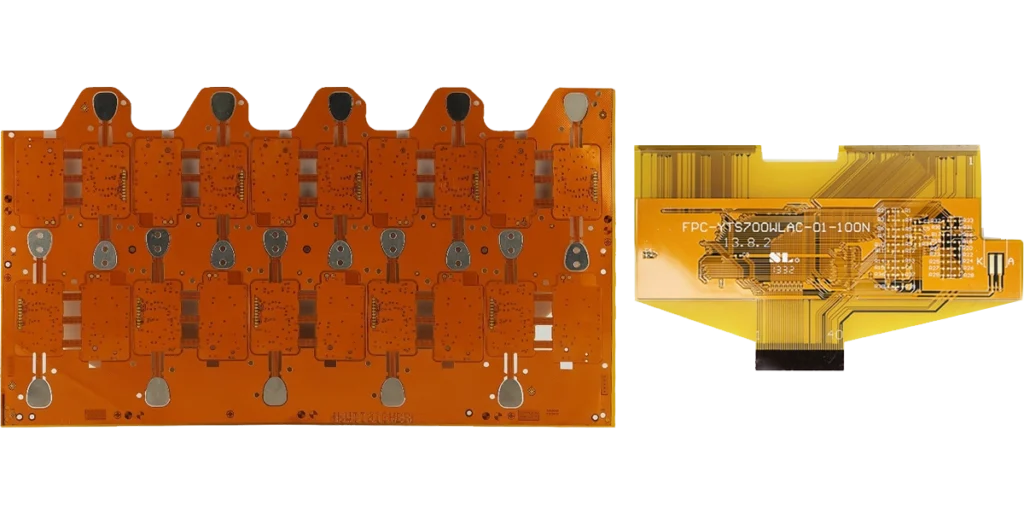
What are Flex PCBs made of?
Flex PCBs are made from a combination of copper foil, film, and polyester or polyimide film. The copper foil is etched to create the circuit design, while the film provides flexibility and shock resistance to the board. The polyester or polyimide film acts as a base for the circuit design and provides the necessary structural support.
Difference Between Rigid PCB And Flexible PCB?
Flex circuits were first used during the Second World War and their use increased rapidly. Over the years, rigid and flexible circuits have enjoyed enormous popularity among military product designers and have also been used in commercial products.
In contrast to rigid circuit boards, flexible circuits are not limited to two dimensions. They can be as flexible as a wire or a ribbon cable, and their design possibilities are endless. Compared to rigid PCBs, the flexible PCB has proven to be more reliable and durable in applications where the circuit is subjected to constant vibration and mechanical stress. Flexible printed circuit board boards are designed with fewer connections which helps to improve the durability of the circuit. Standard joining techniques based on brazed wire and hand-wired connectors are replacing by flexible circuit boards characterized by low weight and thickness, high mechanical resistance, high temperature and weather resistance and good electromagnetic immunity (EMI).
Lightweight
Unlike conventional PCB components, flexible circuits use about 10% of the space and weight of their common counterparts.
Stable
A flexible circuit requires less interconnects, which means that fewer solder joints, connectors, and crimps are required.
Compatibility
Flexible printed circuit boards are incomparable in their compatibility with almost any type of connector or component.
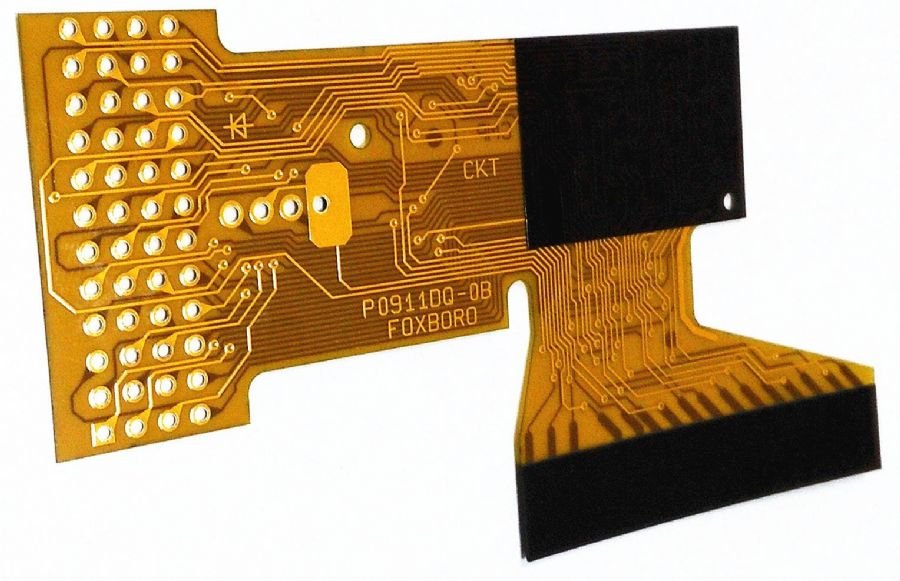
When should you choose Flex PCBs over Rigid PCBs?
While Rigid PCBs have their own set of advantages, Flex PCBs are often the better choice for certain applications:
Compact Designs: If your device requires a highly compact design, where components need to fit into tight spaces, Flex PCB offer unparalleled flexibility and adaptability.
Portable Devices: If your device needs to be lightweight and portable, Flex PCBs are a great choice due to their lightweight and flexible nature.
Cost-Effective: If cost is a factor and you need a PCB that can be easily mass-produced, Flex PCBs may offer a more cost-effective solution.
Customization: If your design requires customization or adaptation to suit specific needs, Flex PCBs provide a highly flexible and customizable solution.
Application Fields We've Served

Computers and Servers
Most commonly used type of circuit board in computers and servers for the manufacture of motherboards, graphics cards, memory modules, and other critical components.

Communication and Networking
Widely used in the communication and networking fields, including the manufacture of routers, switches, base stations, and other communication equipment.
Medical Devices
Can be used to manufacture various medical devices such as diagnostic instruments, therapeutic equipment, monitoring devices, and other medical instruments.

Industrial Control
Can be used in the manufacture of industrial control systems, robots, sensors, and other industrial automation equipment.

Automotive Electronics
Widely used in automotive electronics for the manufacture of engine control modules, airbag control modules, in-car entertainment systems, and other vehicle-mounted electronic devices.

Aerospace
Can be used in the manufacture of flight control systems, communication equipment, and navigation systems for aircraft and spacecraft.

Home Appliances
Can be used in the manufacture of circuit boards for TVs, refrigerators, washing machines, and other household appliances.

Consumer Electronics
Commonly used in consumer electronics for the manufacture of circuit boards that require high performance and reliability. such as smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, and other portable electronic devices.

Power & New Energy
Used in power and renewable energy sectors for a range of applications, including production of high-voltage and low-voltage switchgear, transformers, and other components requiring precise wiring and reliable connections.

 English
English
 中文
中文