High-frequency PCB boards are specialized circuit boards designed to handle signals with frequencies above the traditional range. They are meticulously engineered to minimize signal loss, ensure optimal signal integrity, and manage electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI). These boards are essential for applications demanding fast data transfer, high-speed communication, and wireless connectivity.
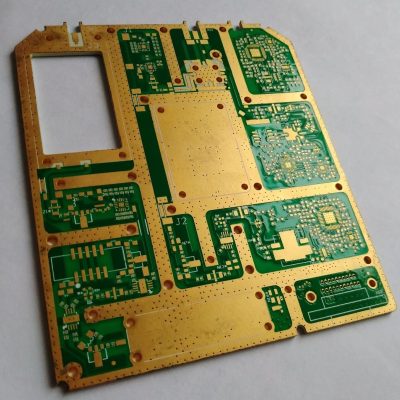

What are the materials used to make high-frequency PCB boards?
The performance of high frequency boards in wireless or other high frequency applications does depend on the building materials chosen. Choosing the right building materials is critical to the performance and reliability of high-frequency circuits. For many applications, using laminated FR4 materials can improve dielectric properties. When manufacturing high-frequency PCB boards, commonly used boards include PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), FR-4 with High-Tg (Glass-Reinforced Epoxy with High Glass Transition Temperature), Rogers PCB Materials, Isola’s I-Tera® Materials, Liquid Crystal Polymer ( LCP), Ceramic-filled materials, etc. It’s important to note that the selection of materials depends on the specific requirements of the high-frequency PCB design, including frequency range, signal integrity, thermal management, and cost considerations.
The dissipation factor (DF) level of general materials directly determines the performance of PCB.
DF (Dissipation Factor):The DF, also known as the loss tangent, is an important parameter that characterizes the energy loss in a material. While the dissipation factor does play a role in determining the performance of PCBs, it is not the sole factor that directly determines their overall performance.
In high-frequency applications, low-loss dielectric materials are preferred to minimize signal attenuation and maintain signal integrity. The dissipation factor is an indicator of the energy lost as heat during signal transmission, and materials with lower dissipation factors generally exhibit lower signal loss. However, it is important to note that other factors, such as the dielectric constant, thermal stability, and consistency of the material, also significantly impact the performance of high-frequency PCBs.
The selection of materials for high-frequency PCBs involves considering multiple parameters, including the dissipation factor, dielectric constant, thermal stability, and mechanical properties. It is a balanced approach that takes into account the specific requirements of the application and the desired performance characteristics.
Therefore, while the dissipation factor is an important parameter, it is not the sole determinant of PCB performance. The overall performance of high-frequency PCBs relies on a combination of factors, including the choice of materials, proper design techniques, impedance control, signal integrity management, and thermal considerations.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: The coefficient of thermal expansion should closely match that of copper foil in order to prevent separation of the copper foil during thermal cycling.
DK (Dielectric Constant): The DK of the material, which represents its ability to store charge, should be low and sufficiently stable. A lower DK is generally preferred as high DK can lead to signal propagation delays.
Good Thermal Resistance, Chemical Resistance, Impact Resistance, and Peel Strength: These properties are crucial for high-frequency PCBs to withstand thermal stress, resist chemical corrosion, withstand mechanical impact, and maintain strong adhesion between layers.
The thermal expansion coefficient of the high-frequency PCB should closely match that of the copper foil to ensure that the performance of the PCB is not affected during thermal cycling. High-frequency PCBs exhibit excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance, impact resistance and peel strength.
Advantages that make high frequency PCB boards so popular in various applications
Enhanced Signal Integrity: High-frequency PCB boards are designed to minimize signal loss and maintain excellent signal integrity at higher frequencies. They offer lower dielectric loss, reduced crosstalk, and improved impedance control, resulting in reliable and high-quality signal transmission.
Wide Frequency Range: High-frequency PCB boards are capable of operating in a wide frequency range, making them suitable for applications involving radio frequencies (RF), microwave frequencies, and beyond. They enable the development of wireless communication systems, radar systems, satellite communication, and other high-frequency applications.
High-Speed Data Transmission: With the increasing demand for high-speed data transfer, high-frequency PCB boards play a critical role in enabling faster data rates. They provide the necessary characteristics, such as controlled impedance and low signal distortion, to support high-speed data transmission in applications like telecommunications, data centers, and high-speed digital circuits.
Miniaturization and Integration: High-frequency PCB boards allow for compact designs and integration of complex circuits. Their improved electrical properties, such as lower dielectric constant and loss tangent, enable the realization of smaller and more efficient electronic devices, particularly in industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
RF and Microwave Performance: High-frequency PCB boards excel in RF and microwave applications, where precise signal control and stability are essential. They can handle high-power RF signals, exhibit minimal RF losses, and provide consistent performance across a range of frequencies.
Design Flexibility: High-frequency PCB boards offer design flexibility, allowing for the implementation of intricate circuit layouts, controlled impedance traces, and precise signal routing. They can accommodate complex designs with multiple layers, high-density interconnects, and advanced features like microvias and blind/buried vias.
Thermal Management: Effective thermal management is crucial in high-frequency applications. High-frequency PCB boards can incorporate thermal vias, heat sinks, and other thermal management techniques to dissipate heat efficiently, ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic components.
Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: High-frequency PCB boards are compatible with advanced technologies like 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and wireless communication protocols. They provide the necessary platform for the development of advanced electronic systems and support the evolving needs of modern technology.
In summary, high-frequency PCB boards offer enhanced signal integrity, wide frequency range, high-speed data transmission, miniaturization capabilities, RF and microwave performance, design flexibility, thermal management, and compatibility with advanced technologies. These advantages have made high-frequency PCB boards highly sought after in various industries and applications, driving their popularity in the PCB field.
Ucreate International Co., Ltd is mainly engaged in 2-32 layer high-frequency printed circuit boards, a powerful manufacturer of quick samples and small and medium-sized batches. Specializing in the production of high-frequency, high-precision, high-density environmentally friendly PCB circuit boards. The main products include: high-frequency PCB circuit boards, Rogers/Rogers high-frequency boards, Taconic/Taconic high-frequency boards, F4B/Teflon high-frequency boards, microwave radio frequency boards, special circuit boards, etc. A high-quality high-frequency PCB board manufacturer. Welcome to contact us if any question about electronic project. You may send email to sales@ucpcba.com,we will provide reliable electronic manufacturing service solutions for you.

 English
English
 中文
中文