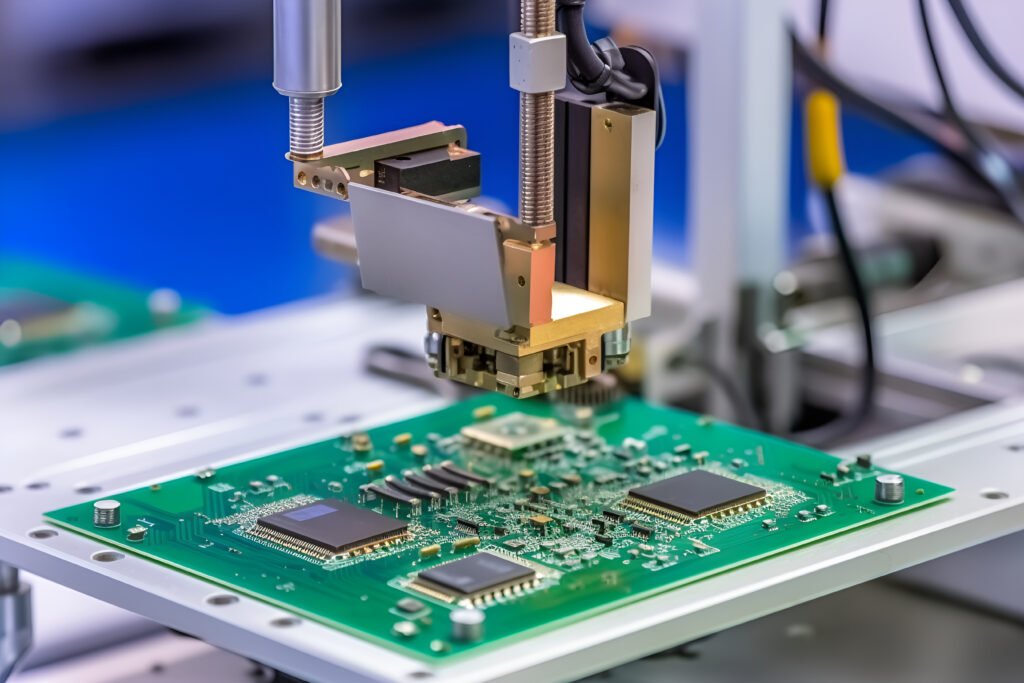
I. Analysis of Selective Welding Technology
Selective soldering, also known as miniature wave soldering, is a more delicate method of soldering in which molten solder is precisely sprayed onto a specified joint through a special nozzle, and the selective soldering system can be programmed to set the length of time and applied solder temperature to provide the best possible results economically and consistently.This is the only technique that allows repeatable soldering of THT components to double-sided PCB assemblies.
II. Welding process
Firstly, special equipment is used to accurately spray flux on the lower part of the PCB to be soldered according to programmed instructions; then the PCB is preheated to activate the flux and reduce thermal shock during soldering; and then soldering is carried out using position-specific solder nozzles.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages: suitable for high-density, fine-pitch through-hole component soldering, can accurately control the soldering area, will not make the component overheating; can achieve higher soldering quality, for example, by controlling the shape of the solder joints to prevent bridging, soldering through the tin rate is high; suitable for mixed PCB soldering, can be well combined with the surface mount technology (SMT).
- Disadvantages: equipment is relatively complex, high cost; programming and operation requirements are high, requiring professional and technical personnel to operate and maintain; welding efficiency is relatively low compared to wave soldering, especially for large-scale, simple through-hole components welding advantages are not obvious.
Third, compare the core advantages of wave soldering
Dimension | SelectiveSoldering | Conventional wavesoldering | Description |
Soldering accuracy | Support 0.3mm pitch pin soldering | Suitable for >0.8mm pitch pins | Selective soldering to meet micro-pitch component soldering requirements, wave soldering prone to bridging (defect rate 3408ppm vs 400-1000ppm) |
Thermal shock control | Thermal impact radius <3mm | Thermal shock wave and full board | Suitable for microprocessors and other components with poor heat resistance |
Capacity adaptability | Flexibility in line modification, high investment in equipment | Low initial investment, high efficiency of mass production | Selective soldering is suitable for multi-species small batch production, wave soldering is suitable for standardised products. |
Rework efficiency | Individual solder joints can be reworked independently, up to 50 times faster. | Requires complete removal and re-soldering | Reduced maintenance costs (e.g. 83% reduction in rework time for PGA devices) |
Environmental Indicators | Flux consumption ↓70%, NMP residue <50ppm | High volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions | Meets RoHS and WEEE directives, reducing waste disposal costs |
IV. Combination of wave soldering and selective soldering
In actual production, wave soldering and selective soldering are not mutually exclusive, but can be used in combination with each other.
For example, for a large number of simple through-hole components and high-density, fine-pitch chip components and through-hole components mixed PCB board, you can first complete most of the simple through-hole components through the wave soldering welding, and then use selective soldering on the complexity of the region for accurate welding.This combination can give full play to the efficient advantages of wave soldering, but also with the accuracy of selective welding advantage, improve the overall welding quality and production efficiency.
V. Conclusions
Although wave soldering and selective soldering each have their own characteristics and application scenarios.However, selective soldering is still reshaping the landscape of high-density electronic assembly process by virtue of its precise and controllable, environmentally friendly features.When selecting the soldering process for through-hole components, it is necessary to consider various factors such as production scale, product requirements, and cost.With the development of semiconductor technology to a higher degree of integration, selective welding technology will play a key role in new energy vehicles, AI edge computing and other fields, and its process optimisation and equipment cost reduction will promote the manufacturing industry to “precision + green” dual transformation.

 English
English
 中文
中文