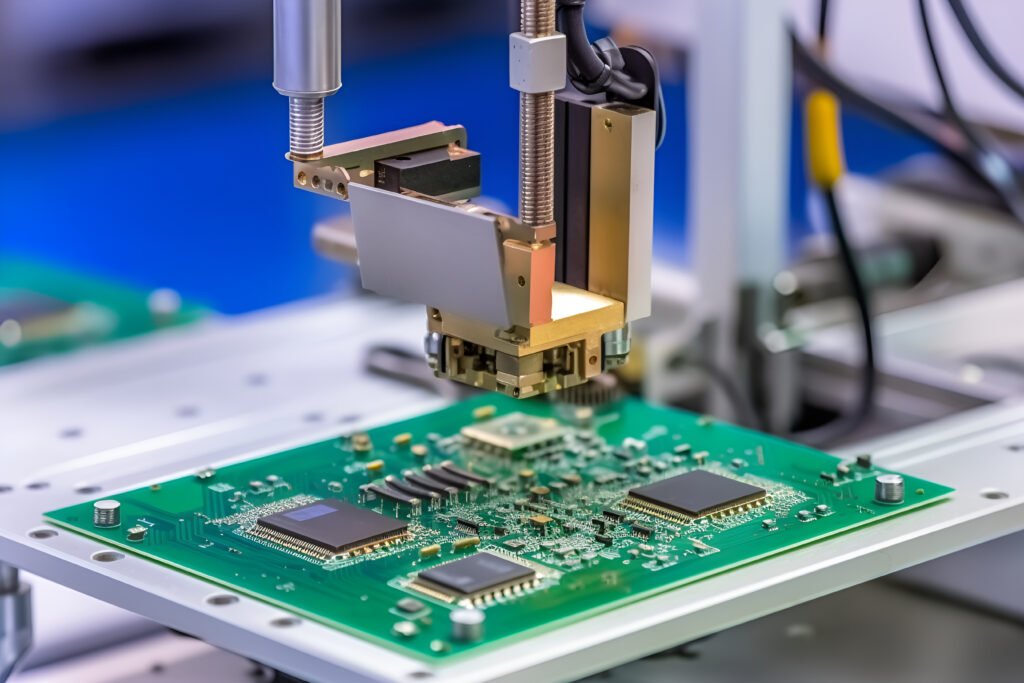
Rigid-Flex PCB is a new type of electronic circuit board that combines traditional rigid circuit board (PCB) with flexible circuit board (FPC). Its basic principle is to combine materials with different characteristics through lamination, layering, etc. to form a circuit board with complex electrical connections and mechanical structures. Rigid-flex PCB is widely used in communication equipment, medical equipment, automotive electronics, aerospace and other fields. Due to its unique design flexibility and high performance, it is gradually becoming an important development trend in the electronics industry.
Characteristics and advantages of rigid-flex boards
rigid flexible PCB boards have significant characteristics and advantages in the design and manufacturing process. First, rigid-flex boards have the advantages of both rigid and flexible boards, and can achieve highly integrated and lightweight design, effectively reducing product volume and weight. Secondly, rigid-flex boards have the advantages of high reliability, high density, and high heat dissipation, and can meet the needs of complex electrical connections and mechanical structures. In addition, rigid-flex boards also have good flexibility and foldability, adapting to various complex shapes and layouts, providing more possibilities for product design and manufacturing.
The manufacturing process of rigid-flex circuit boards rigid flex pcb manufacturing is a complex and sophisticated process involving multiple links and steps. The following are the main processes of rigid-flex circuit board manufacturing, combined with relevant figures and information for detailed explanation:
1. Design stage
(1) Circuit diagram design: First, electronic engineers design circuit diagrams according to product requirements and determine the functional modules of hardware and software.
(2) Schematic design: Convert functional modules into specific circuit connections to form a complete circuit schematic.
(3) PCB layout design: Arrange each functional module on the circuit board according to certain rules, and optimize the layout to improve space utilization.
(4) PCB wiring design: According to the circuit schematic, arrange the connection lines between components on the circuit board to ensure the stability and reliability of the circuit.
2. Raw material procurement
(1) Hard board materials: Commonly used hard board materials include FR-4 glass fiber film and metal substrate. When purchasing, you need to consider their quality, performance and price.
(2) Flexible circuit board materials: mainly polyimide (PI) film, and you also need to pay attention to its quality, thickness and performance:
(3)Other materials: such as heat-resistant glue, electroplating solution, chemical reagents, etc., are also indispensable materials in the manufacture of soft and hard circuit boards.
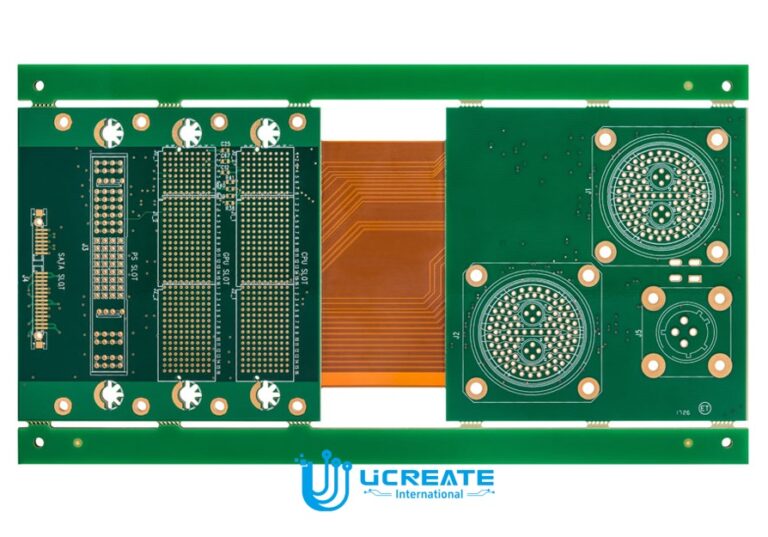
3. Manufacturing process
(1) Hard board processing
Sheet cutting: Cut the whole large sheet into small sheets as required according to the design requirements.
0 Punching and slotting: Punch and slot on the hard board to arrange the wiring and install electronic components.
Pressing: Reserve the bending space of the flexible circuit board on the hard board to ensure that the flexible circuit board can be bent and fixed smoothly.
External circuit pattern stamping: Stamp the circuit pattern on the surface of the hard board.
(2) Flexible circuit board production:
Coating: Lay the polyimide film and the base material together to form a substrate, and then coat the photosensitive copper film. Printing, photolithography.
Etching: Through printing, photolithography and etching processes, a flexible circuit diagram is formed
Outer circuit diagram embossing: Circuit diagrams are embossed on the flexible circuit board.
(3) Soft-hard combination:
Hot pressing technology: The flexible circuit board is combined with the hard board through hot pressing technology, while ensuring that the bending space reserved for the flexible circuit board on the hard board is bent and fixed. Conductive connection: The hard board with holes drilled and the flexible circuit board with copper cladding and punching are connected by several methods such as conduction to form a complete circuit system.
(4)Surface treatment: In order to improve the performance and service life of the circuit board, surface treatment is required, such as tin spraying, gold spraying, chemical deposition, surface corrosion protection, etc.
(5) Inspection and testing: Through visual inspection, electrical performance testing, functional testing and other methods, the circuit board is comprehensively inspected and tested to ensure that the specified standards and requirements are met.
4. Summary
The manufacturing process of hard-and-soft circuit boards covers the entire process from the design stage to raw material procurement, manufacturing process and inspection and testing. Each link requires fine operation to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
With the rapid development of technologies such as 5G, Internet of things, and artificial intelligence, the performance requirements for electronic products are constantly increasing, and hard-and-soft circuit board technology will usher in a broader application prospect. In the future, hard-and-soft circuit board technology will develop towards higher integration, higher reliability, and higher performance.
Ucreate is one of the best rigid-flex PCB manufacturer in China. We can produce 2-64 layers rigid-flex pcb prototype and mass prodcution. Min. Hole Size can be increased by 0.05mm. Send PCB Files to Sales@ucpcba.com, We Will Quote You Very Soon!

 English
English
 中文
中文